As I sit down to write this, world have departed COP26 in Glasgow, leaving their appointed diplomats and negotiators to begin critical multilateral discussions aimed at getting the world on track to net-zero emissions.

This is where the real work begins towards limiting global warming in line with the Paris Agreement and shaping a more sustainable world.
All forms of transportation account for about 24% of all CO2 emissions worldwide, with around 75% of this from road transportation1. The role of the paving industry is therefore critical to addressing global sustainability challenges by decarbonising road construction, while continuing to improve performance.
The future is about more than decarbonisation
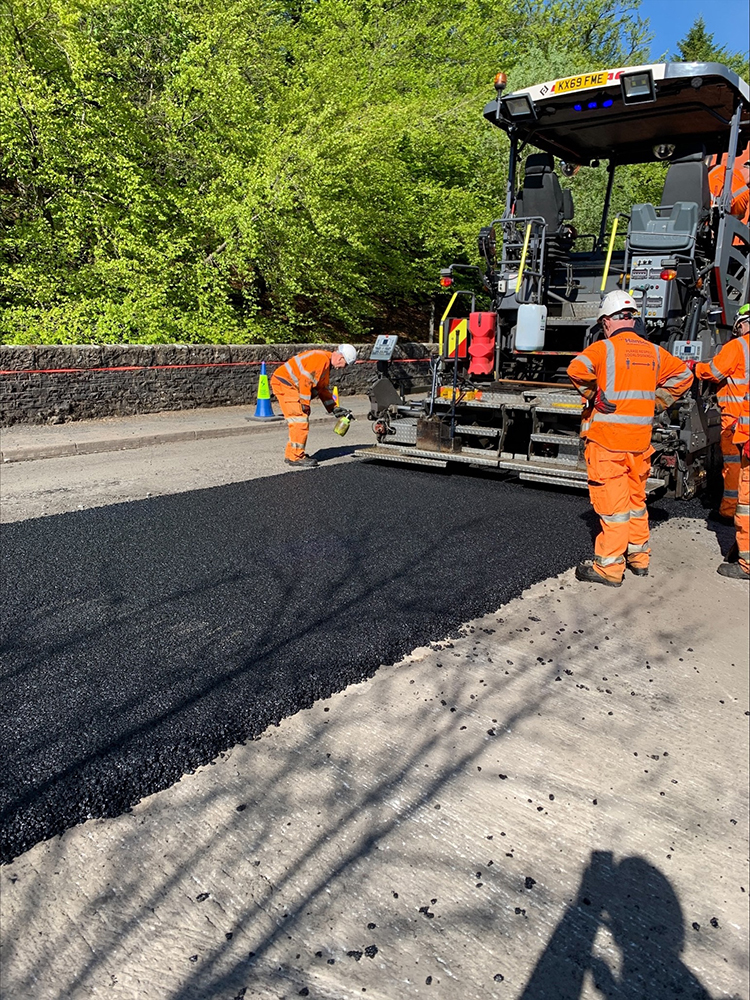
We are excited to launch Shell Bitumen LT R, our new circular product for roads that has been specifically designed to play a part in addressing the issue of waste plastic. Shell Bitumen LT R is a low-temperature binder with an additive that is chemically converted from waste plastic and blended into the bitumen, saving an estimated 450kg of plastic waste and a tonne of CO2-equivalent emissions per kilometre of road paved2.

Converting non-recyclable plastic bottles destined for landfill to a bespoke bitumen additive improves circularity and also performance. When carefully incorporated LT R is easy to mix, evenly dispersed and stable, and retains the lower production and laying temperatures of the LT technology Shell Bitumen has pioneered for more than 25 years.
Why is this important? Innovations such as this will help our customers and clients to meet the UK government’s target to halve the amount of municipal waste going to landfill by 2035. Creating a new end-market for non-recyclable waste plastic also helps mitigate the climate impact of global plastics production.
Wear and tear on highways
The pressure on road paving is increasing for a variety of reasons including climate change and rising average ambient air temperatures. Roads are not designed to withstand this, leading to early-life surface rutting and deformation that has to be repaired more frequently, and that is not sustainable.
The new generation of fuel-efficient autonomous vehicles, whether they be hybrid or fully electric, represent another significant challenge when it comes to road maintenance. Autonomous vehicles will move very close together one after the other in a ‘canalised’ fashion, with very few rest periods.

While this may be good for both commuters and the environment, it will inevitably place additional strain on road networks because all of that stress is being exerted by vehicles on the pavement in exactly the same points on the road surface every time, which will lead to more early-life failures.
The transition from conventional dual-wheel axles on vehicles to super single tyres, while undeniably good in terms of reducing tyre wear, also results in higher levels of pavement damage. Similarly, leaks from poorly maintained air suspensions can lead to steel-on-steel contact instead of a cushioned load, meaning the actual peak loads being applied on the road surface are much higher.
We are also witnessing a tendency for haulage companies to carry more freight on a single vehicle. Again, this is good for the environment, but the increased weight can lead to more road damage.
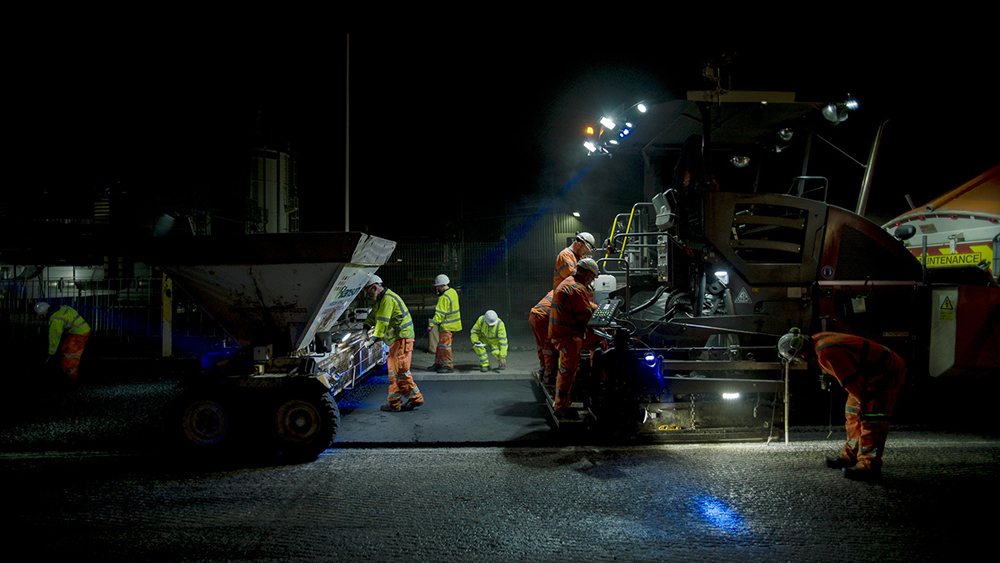
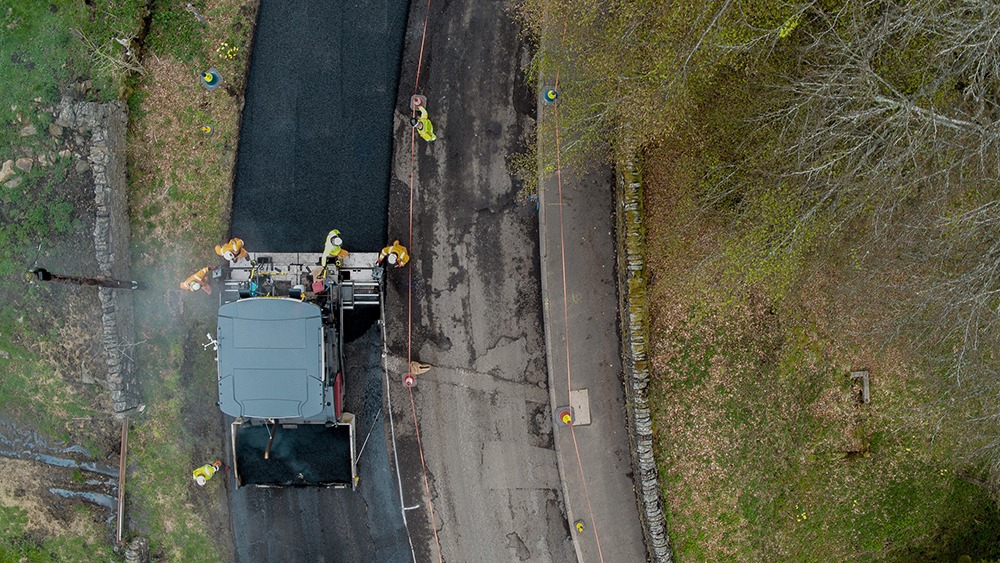
Putting Shell Bitumen LT R to the test
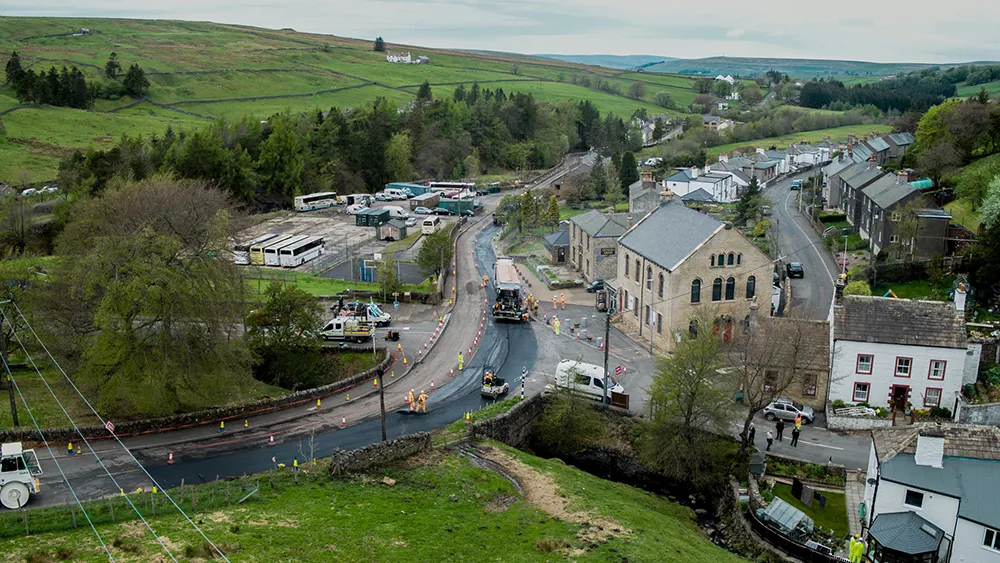
We are putting Shell Bitumen LT R through its paces in Cumbria to demonstrate its real world environmental and operational benefits in one of the UK’s harshest driving environments. Started in May 2021, Shell partnered with Cumbria County Council and UK contractor Hanson to lay miles of urban and rural roads in a project funded by the ADEPT Live Labs programme.

“What is fundamental to this pilot… is the huge volume of waste plastics, which are stopped going into landfill, which is a major benefit to Cumbria and the UK,” commented Councillor Keith Little, who works on the county’s highways and transport portfolio.
The road paving industry has a key role to play in this sustainable future, and I am proud that we are continuing to lead the way in developing innovative, impactful solutions that empower our customers to make positive changes now.
Sources:
1 World Resources Institute
2 Shell Construction & Road
Sponsored content produced in association with Shell