The agreement aims to increase intra-African trade by eliminating import duties. Its planners hope to double intra-African trade if non-tariff barriers are also reduced; a major milestone in the continent’s regional integration. However, inadequate transport infrastructure and services could hamper the realisation of AfCFTA’s benefits. The urgent need to improve transport connectivity in Africa in the context of AfCFTA has created new research demands.
In this regard, the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) has undertaken research to explore the effects of AfCFTA on trade flows in Africa. The research also examines how the AfCFTA signatories could reap the agreement’s full benefits through the integrated planning of trade and transport.
The study has enabled ECA to:
- Forecast the demand for different modes of transport — road, rail, maritime and air —because of AfCFTA.
- Estimate the infrastructure investments required for different modes of transport.
- Estimate the impact of improvements in transport infrastructure and services on the volume of intra-African trade.
- Forecast the demand for equipment for different modes of transport — trucks for roads, rolling stock for railways, aircraft for air transport, and ships for maritime transport —because of AfCFTA.
The research shows that introduction of the AfCFTA will lead to a general increase in intra-African freight demand of around 28%, compared with a scenario without the AfCFTA.
Currently, intra-African freight transport demand is heavily skewed towards road transport (77%), with rail’s share close to 0% (figure 1).
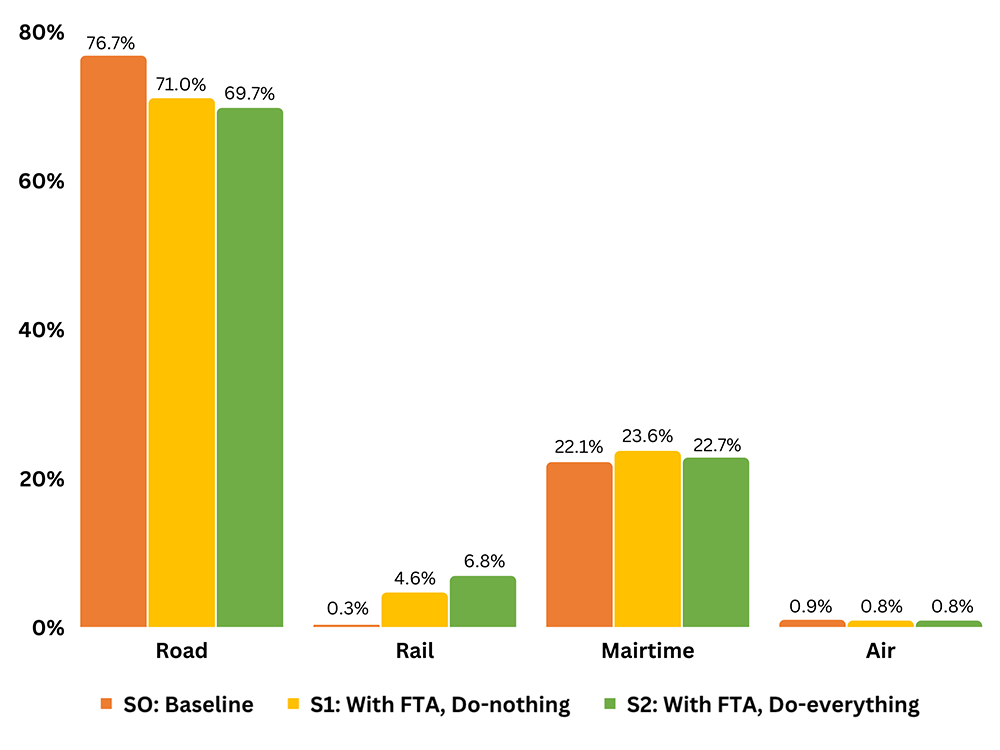
African transport policies to expand the rail network, combined with trade policies to implement the AfCFTA, are expected to change that distribution.
By 2030, with the AfCFTA implemented and the continent’s plans for freight infrastructure and service improvements realised, the share of rail would increase from 0.3% to about 7%. The share of freight transport by road would decrease from 77% to 70%. The share of freight transport by ship would increase, but without AfCFTA it would be reduced. The air cargo transport mode share would remain almost unchanged from that without AfCFTA.
Up to 57,363km of road require upgrading to accommodate the anticipated increase in freight as a result of AfCFTA. These links are critical to the success of AfCFTA. Some 20,031km of the critical links would be addressed by completing regional infrastructure projects planned for 2030. These are essentially projects of the Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa (PIDA).
It is worth noting that demand for the different modes of transport varies from one region to another and from one trading pair of regions to another. For instance, the largest truck demand to support trade flows is within West Africa, with 39.3%, from West Africa to Southern Africa, with 19.8%, from Southern Africa to West Africa with 9.9%.
For ECA, the report is a useful tool to enhance the effectiveness of its support to member States and to sub-regional and regional organisations when they develop national and regional AfCFTA strategies. The report also supports UNECA’s objective to crowd-fund private sector investment in Africa’s infrastructure development. n
• The full report is available at: https://repository.uneca.org/handle/10855/47596







