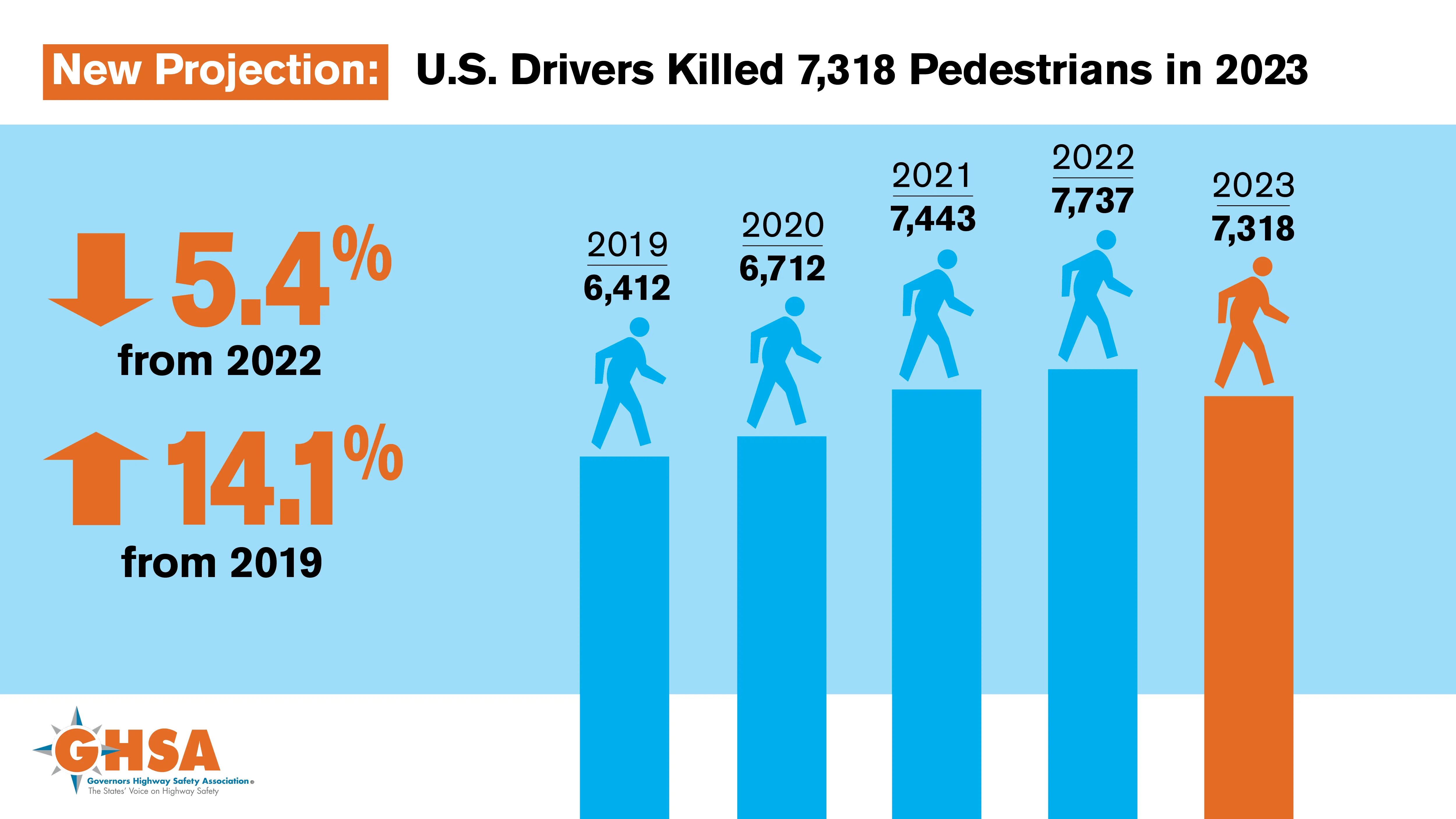
US pedestrian traffic fatalities fell 5% last year but remain 14% above the pre-pandemic level, according to data from the Governors Highway Safety Association, GHSA.
The data analysis also reveals just how much more dangerous it now is to walk in the US, says the association in its report Pedestrian Traffic Fatalities by State: 2023 Preliminary Data. Pedestrian deaths have increased 77% since 2010, compared to 22% for all other traffic deaths.
In 2022, light trucks accounted for 52% of all pedestrian deaths where the vehicle type was known, up from 44% in 2012. Also in 2022, 78% of pedestrian fatalities occur at night and the share of night-time deaths has risen even more in recent years.
The report also highlights trends regarding when, where and how drivers strike and kill people who are walking. The five-year death toll surpasses 35,000 as dangerous driving, infrastructure shortfalls, larger vehicles contribute to perilous conditions for people walking.
Analysis found that drivers struck and killed 7,318 people in 2023 – down 5.4% from the year before but 14.1% above the 2019 pre-pandemic level (see graph). The association says that while this modest year-over-year decrease is welcome news, pedestrian fatalities have been surging in recent years and reached a 40-year high in 2022.
The GHSA’s report is based on preliminary data reported by the State Highway Safety Offices (SHSOs) in all 50 states and the District of Columbia (DC) and builds upon a report the association issued earlier this year. The new report also includes an in-depth analysis of 2022 data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) that reaffirms some troubling trends regarding deaths of people on foot happening at night, where there are no sidewalks and in crashes with SUVs and pickups. The data analysis was conducted the research firm Westat.
“A decline in pedestrian deaths offers hope that after years of rising fatalities a new trend is starting,” said Jonathan Adkins, chief executive of the GHSA. “We know how to improve safety for people walking – more infrastructure, vehicles designed to protect people walking, lower speeds and equitable traffic enforcement. It will take all this and more, to keep the numbers going in the right direction.”
In addition to providing a first look at state-level fatality figures, the GHSA report examines 2022 data from NHTSA’s Fatality Analysis Reporting System (FARS) that examines when, where and how drivers strike and kill people on foot. According to this analysis, pedestrian deaths are increasing at a rate far faster than overall traffic fatalities.
Between 2010 and 2022, pedestrian deaths rose 77%, while all other traffic fatalities increased 22%. There were 135 more pedestrian deaths in 2022 compared to the year before, while there were 628 fewer fatalities from all other traffic crashes.
The number of pedestrian deaths involving passenger cars and light trucks - which include SUVs, pickups and vans - were largely similar for much of the 2010s. Beginning in 2020, however, light trucks accounted for a much larger share of pedestrian fatalities as their proportion of US new vehicle sales continued to climb. In 2022, light trucks accounted for 52% of all pedestrian deaths where the vehicle type was known, up from 44% in 2012.
The vast majority - 78% in 2022 - of pedestrian fatalities occur at night and the share of nighttime deaths has risen even more in recent years. Nighttime fatal pedestrian crashes nearly doubled from 3,030 in 2010 to 5,798 in 2022. This is a 92% increase, compared to a 28% increase in daylight fatalities - from 1,092 in 2010 to 1,401 in 2022.
Multiple studies have documented that people of colour are overrepresented in pedestrian fatalities. Race and ethnicity data for 2022 pedestrian deaths were not available in NHTSA’s Fatality Analysis Reporting System due to delays in processing death certificates. But researchers looked at changes between 2019 and 2021 And found that deaths involving pedestrians whose race was reported as white non-Hispanic fell from 43% to 40%, while they rose from 19% to 21% for Black non-Hispanic pedestrians.
In 2022, two-thirds (66%) of pedestrian fatalities occurred in locations where no sidewalk was noted in the crash report, up from 59% in 2017. Sidewalks (pavements, in the UK) can help protect people walking by providing a physical separation between them and motor vehicle traffic. But they are missing or in poor condition in many parts of the country. More than three-quarters (76%) of pedestrian deaths in 2022 were not at an intersection.
Non-freeway (motorway) arterial roads, which typically carry large volumes of traffic at high speeds, are the most dangerous for people on foot, accounting for 60% of all fatalities in 2022. More than 1,300 deaths (18%) were on freeways. Stranded motorists exiting their vehicles, first responders and tow truck drivers are all examples of pedestrians who have been killed on freeways. All states have Move Over laws, but they are difficult to enforce. Digital alerting technology that warns drivers of vehicles on the roadside can help reduce these types of crashes.
In 2022, 30% of pedestrians 16 and older killed in motor vehicle crashes had a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.08 or higher. Looking at driver impairment, around 19% of fatal pedestrian crashes involved a driver with a BAC over 0.08. Alcohol and/or drug impairment by pedestrians can put them at risk while walking near vehicle traffic, but drivers bear the brunt of responsibility as the operators of multi-ton machines with the kinetic potential to kill or injure someone.
The Governors Highway Safety Association is a nonprofit association representing the highway safety offices of states, territories, the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico.





