The World Bank Global Road Safety Facility and IRF work together to reduce the toll of road deaths and serious injuries in low and middle-income countries
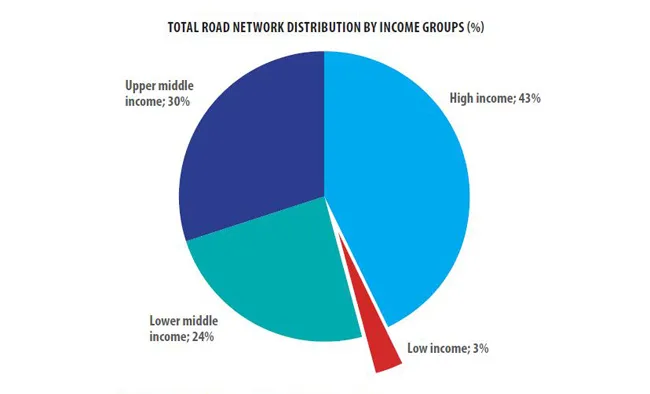
With more than 1.2 million people dying and over 50 million injuries occurring every year, the economic and social costs of road accidents are simply too high. They have a disproportionate impact on the poor and can plunge households into poverty.
The economic costs of road traffic deaths and injuries in low and middle-income countries are estimated at USD 65 billion a year. Moreover, the global cost of road traffic injuries is predicted to increase by more than 65% by 2020. By 2030, road traffic deaths and injuries are expected to be the fourth major cause of loss of healthy years for the general population, and the number two cause of death for men.
The death of a breadwinner presents an ominous and daunting challenge for those that are left behind, or who are left to deal with a disabled family member.
A Global Responsibility
To combat this growing epidemic, TheThe Facility has partnered with
Two modules have been created: Designing Safer Roads for Vulnerable Road Users and Roadside Safety Design.
"These modules introduce simple, low-cost engineering measures that will save thousands of lives, provide a better standard of living and accomplish the World Bank's goals", said Patrick Sankey, President & CEO of IRF-Washington.
Safer Roads Save
Lives IRF presented the first course, Designing Safer Roads for Vulnerable Road Users (VRU) to two audiences. The first VRU course was presented in Accra, Ghana, to a gathering of 30 road officials, law enforcement officers, engineers and other road professionals concerned over the high number of crashes, injuries and fatalities affecting VRU in Ghana. The second VRU course was delivered in Bogotá, Colombia, to a group of 40 delegates.Each course included in-depth discussions on the GRSF Infrastructure Safety Management, VRU planning and design considerations, diagnosing VRU issues, potential countermeasures and steps to develop a VRU Safety Action Plan.
"This course proved to be very relevant," said Noble J. Appiah, Executive Director of the National Road Safety Commission of Ghana.
"The training really addressed one of the key challenges facing road safety management in Ghana - designing roads with the vulnerable road user in mind."
IRF Geneva elects new Chairman
As delegates began to gather in Lisbon for the IRF World Meeting, the Federation's Geneva Programme Centre proceeded with the election of a new Chairman to guide the organisation into the next decade.
The overwhelming vote went to Mr. K. K. Kapila, the Chairman and Managing Director of ICT Pvt. Ltd., a New Delhi based firm that has been ranked among the top hundred consultancy companies in the world, and which operates in more than 30 countries.
Already a member of the IRF Geneva Board of Directors, and Vice-Chairman since 2007, Mr. Kapila's nomination earned him the distinction of becoming the first non-European to be elected to this key responsibility.Participants in the two courses also conducted assessments and field visits in downtown Accra and Bogotá respectively, where they were able to apply some of the concepts learned to real-world situations.
Upon completion of the courses, participants were able to define vulnerable road users; describe VRU needs; diagnose crash causes and select proper countermeasures; identify safety-related geometric design elements; and discuss VRU safety issues as well as how to address them.
The second module, Roadside Safety Design, was presented in Kampala, Uganda, and Lima, Peru.
Each course was attended by 40 road professionals, all with a prominent stake in building, designing and maintaining safer roads in their respective countries.
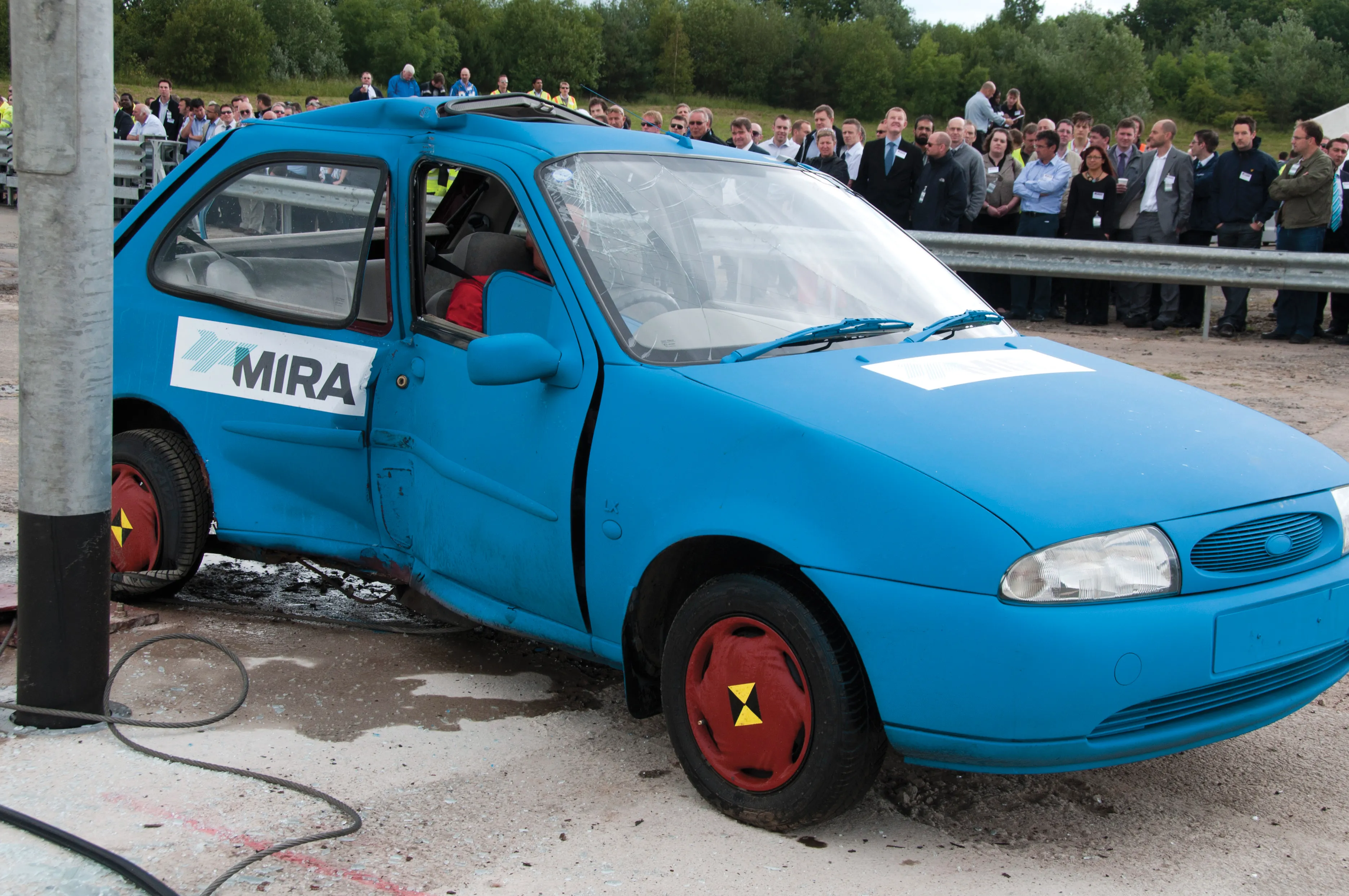
This module imparted the necessary knowledge and skills needed to identify safety issues associated with roadside design, impacts on highway safety and the selection of appropriate hardware (barriers, crash cushions and impact attenuators). It included extensive discussion of the GRSF Infrastructure Safety Management, clear zones, crash testing and breakaway devices, roadside barriers, end treatments, crash cushions and procurement considerations.
As with the VRU module, participants in Uganda conducted a field visit and assessment of new roadways in Kampala, where they applied some of the concepts learned to real-world situations, and attendees in Lima conducted a field visit and assessment of the Pan American Highway near San Bartolo.
Upon completion, participants were able to define the role of the roadside as it relates to traffic safety; understand and apply the clear zone concept; decide which roadside design strategy is most appropriate for a given situation; ensure proper placement of roadside hardware; select and design roadside and median barriers; and choose the most appropriate barrier end treatment.
"The course content was excellent," said Jorge Lazarte, President of the Peruvian Roads Association.
"There was so much to process and learn, I wish the course could have been extended by two or three days. This is some much needed training."